[1]:
from mimic.utilities.utilities import set_all_seeds
from mimic.utilities.utilities import plot_gLV
from mimic.model_infer import *
from mimic.model_simulate import *
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.integrate import odeint
WARNING (pytensor.tensor.blas): Using NumPy C-API based implementation for BLAS functions.
Simulate some time course data from the gLV¶
The generalized Lotka-Volterra equation takes the form
\[\frac{dX_i}{dt} = \mu_i X_i + X_i M_{ij} X_j + X_i \epsilon_{il} u_l\]
where:
\(X_i\) is the concentration of a species
\(\mu_i\) is its specific growth rate
\(M_{ij}\) is the effect of the interaction of species \(i\) on species \(j\)
\(\epsilon_{il}\) is the susceptibility to the time-dependent perturbation \(u_l\)
Model with five species¶
[2]:
set_all_seeds(1234)
num_species = 5
times = np.arange(0, 10, 0.1)
M = np.zeros((num_species, num_species))
np.fill_diagonal(M, [-0.05, -0.1, -0.15, -0.01, -0.2])
M[0, 2] = -0.025
M[1, 3] = 0.05
M[4, 0] = 0.02
# construct growth rates matrix
mu = np.random.lognormal(0.01, 0.5, num_species)
# construct perturbation matrix
npert = 1
epsilon = np.zeros([num_species, npert])
epsilon[:, 0] = [1.0, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0]
# create a perturbation function including a perturbation at t=2, t=3 and t=4
def pert_fn(t):
if 2.0 <= t < 2.2 or 3.0 <= t < 3.2 or 4.0 <= t < 4.2:
return np.array([1])
else:
return np.array([0])
# write the mu, M, epsilon, and pert_fn to a dictionary and pickle
params = {'mu': mu, 'M': M, 'epsilon': epsilon }
pd.to_pickle(params, 'params-s5.pkl')
Simulate single time course¶
[3]:
# initial conditions
init_species = 10 * np.ones(num_species)
# instantiate simulator
simulator = sim_gLV(num_species=num_species,
M=M,
mu=mu)
simulator.print_parameters()
yobs, init_species, mu, M, _ = simulator.simulate(times=times, init_species=init_species)
# add some gaussian noise
yobs = yobs + np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=0.1, size=yobs.shape)
# plot simulation
plot_gLV(yobs, times)
# write the data out
df = pd.DataFrame(yobs, columns=[f'species_{i+1}' for i in range(num_species)])
df['time'] = times
cols = df.columns.tolist()
cols = cols[-1:] + cols[:-1]
df = df[cols]
df.to_csv('data-s5-r1.csv', index=False)
Model parameters:
Model: gLV
num_species: 5
mu: [1.28 0.56 2.07 0.86 0.7 ]
M: [[-0.05 0. -0.03 0. 0. ]
[ 0. -0.1 0. 0.05 0. ]
[ 0. 0. -0.15 0. 0. ]
[ 0. 0. 0. -0.01 0. ]
[ 0.02 0. 0. 0. -0.2 ]]
epsilon: []
Using the following parameters for gLV simulation: {'num_species': 5, 'mu': array([1.27853844, 0.55683415, 2.06752757, 0.86387608, 0.70448068]), 'M': array([[-0.05 , 0. , -0.025, 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , -0.1 , 0. , 0.05 , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , -0.15 , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.01 , 0. ],
[ 0.02 , 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.2 ]]), 'epsilon': array([], shape=(5, 0), dtype=float64)}
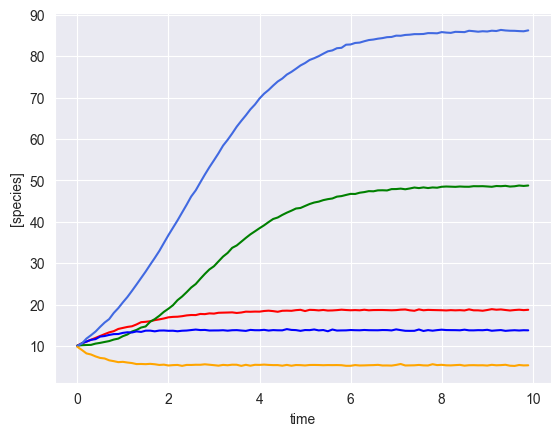
Simulate single time course with a perturbation¶
[4]:
simulator = sim_gLV(num_species=num_species,
num_perturbations=npert,
M=M,
mu=mu,
epsilon=epsilon)
simulator.print_parameters()
yobs, init_species, mu, M, _ = simulator.simulate(times=times, init_species=init_species, u=pert_fn)
# add some gaussian noise
yobs = yobs + np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=0.1, size=yobs.shape)
# plot simulation
plot_gLV(yobs, times)
# write the data out
df = pd.DataFrame(yobs, columns=[f'species_{i+1}' for i in range(num_species)])
df['time'] = times
cols = df.columns.tolist()
cols = cols[-1:] + cols[:-1]
df = df[cols]
df.to_csv('data-s5-r1-p1.csv', index=False)
Model parameters:
Model: gLV
num_species: 5
mu: [1.28 0.56 2.07 0.86 0.7 ]
M: [[-0.05 0. -0.03 0. 0. ]
[ 0. -0.1 0. 0.05 0. ]
[ 0. 0. -0.15 0. 0. ]
[ 0. 0. 0. -0.01 0. ]
[ 0.02 0. 0. 0. -0.2 ]]
epsilon: [[ 1.]
[-1.]
[ 1.]
[-1.]
[ 1.]]
Using the following parameters for gLV simulation: {'num_species': 5, 'mu': array([1.27853844, 0.55683415, 2.06752757, 0.86387608, 0.70448068]), 'M': array([[-0.05 , 0. , -0.025, 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , -0.1 , 0. , 0.05 , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , -0.15 , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.01 , 0. ],
[ 0.02 , 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.2 ]]), 'epsilon': array([[ 1.],
[-1.],
[ 1.],
[-1.],
[ 1.]])}
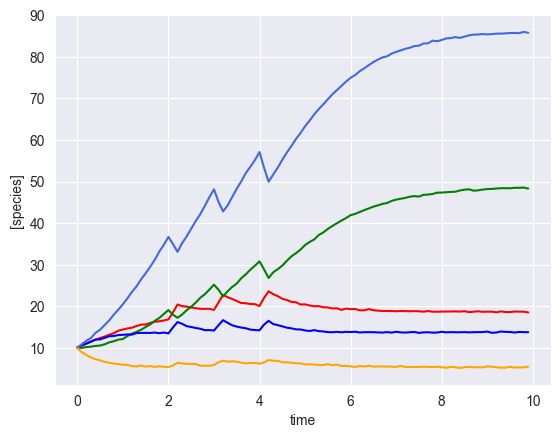
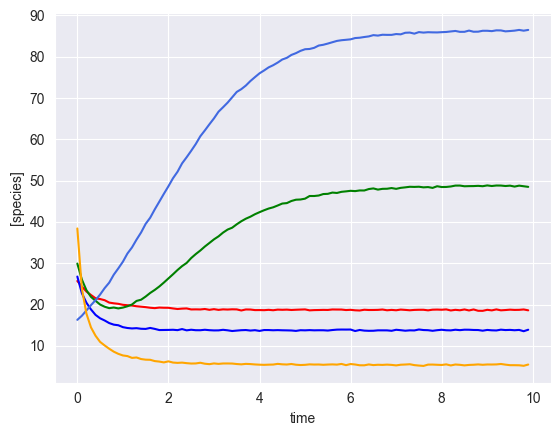
Simulate multiple time courses¶
[5]:
ryobs = []
num_timecourses = 3
for timecourse_idx in range(num_timecourses):
# initial conditions
init_species = np.random.uniform(low=10, high=50, size=num_species)
yobs, init_species, mu, M, _ = simulator.simulate(times=times, init_species=init_species)
# add some gaussian noise
yobs = yobs + np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=0.1, size=yobs.shape)
# plot results
plot_gLV(yobs, times)
# append results
ryobs.append(yobs)
# create a dataframe with times as the first column then the species
df = pd.DataFrame(times, columns=['time'])
for k in range(num_timecourses):
for i in range(num_species):
df[f'species_{i+1}_{k+1}'] = ryobs[k][:, i]
df.to_csv('data-s5-r3.csv', index=False)
Using the following parameters for gLV simulation: {'num_species': 5, 'mu': array([1.27853844, 0.55683415, 2.06752757, 0.86387608, 0.70448068]), 'M': array([[-0.05 , 0. , -0.025, 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , -0.1 , 0. , 0.05 , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , -0.15 , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.01 , 0. ],
[ 0.02 , 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.2 ]]), 'epsilon': array([[ 1.],
[-1.],
[ 1.],
[-1.],
[ 1.]])}
Using the following parameters for gLV simulation: {'num_species': 5, 'mu': array([1.27853844, 0.55683415, 2.06752757, 0.86387608, 0.70448068]), 'M': array([[-0.05 , 0. , -0.025, 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , -0.1 , 0. , 0.05 , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , -0.15 , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.01 , 0. ],
[ 0.02 , 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.2 ]]), 'epsilon': array([[ 1.],
[-1.],
[ 1.],
[-1.],
[ 1.]])}
Using the following parameters for gLV simulation: {'num_species': 5, 'mu': array([1.27853844, 0.55683415, 2.06752757, 0.86387608, 0.70448068]), 'M': array([[-0.05 , 0. , -0.025, 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , -0.1 , 0. , 0.05 , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , -0.15 , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.01 , 0. ],
[ 0.02 , 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.2 ]]), 'epsilon': array([[ 1.],
[-1.],
[ 1.],
[-1.],
[ 1.]])}
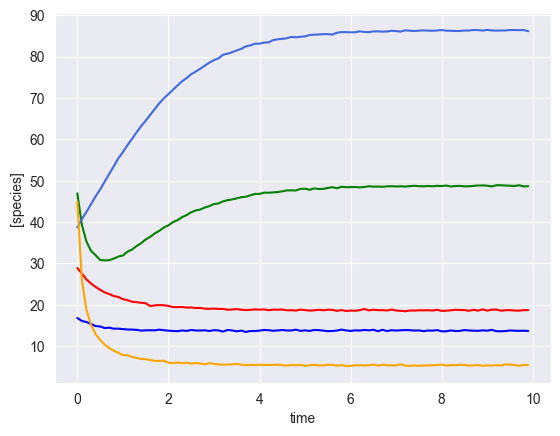
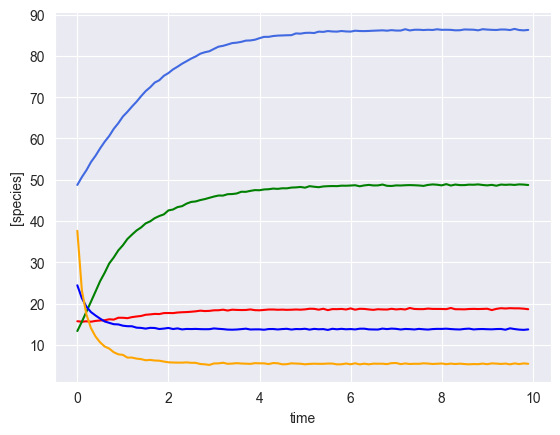
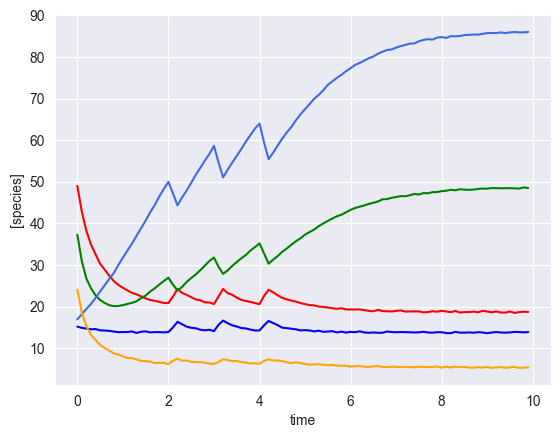
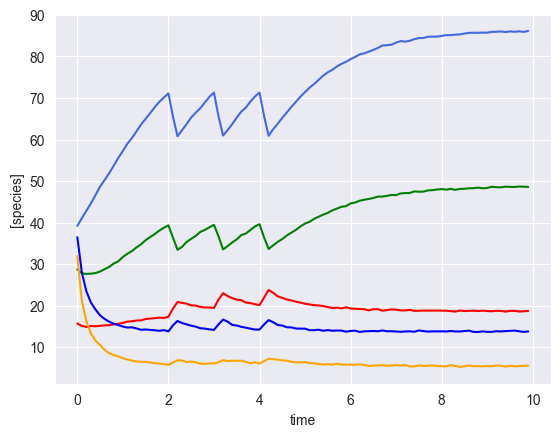
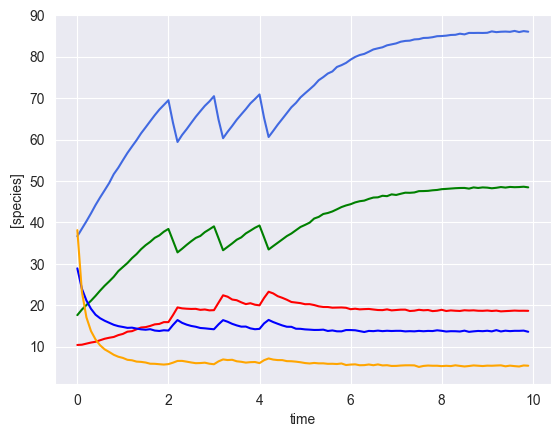
Simulate multiple time courses with a perturbation¶
[6]:
ryobs = []
num_timecourses = 3
simulator = sim_gLV(num_species=num_species,
num_perturbations=npert,
M=M,
mu=mu,
epsilon=epsilon)
simulator.print_parameters()
for timecourse_idx in range(num_timecourses):
# initial conditions
init_species = np.random.uniform(low=10, high=50, size=num_species)
yobs, init_species, mu, M, _ = simulator.simulate(times=times, init_species=init_species, u=pert_fn)
# add some gaussian noise
yobs = yobs + np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=0.1, size=yobs.shape)
# plot results
plot_gLV(yobs, times)
# append results
ryobs.append(yobs)
# create a dataframe with times as the first column then the species
df = pd.DataFrame(times, columns=['time'])
for k in range(num_timecourses):
for i in range(num_species):
df[f'species_{i+1}_{k+1}'] = ryobs[k][:, i]
df.to_csv('data-s5-r3-p1.csv', index=False)
Model parameters:
Model: gLV
num_species: 5
mu: [1.28 0.56 2.07 0.86 0.7 ]
M: [[-0.05 0. -0.03 0. 0. ]
[ 0. -0.1 0. 0.05 0. ]
[ 0. 0. -0.15 0. 0. ]
[ 0. 0. 0. -0.01 0. ]
[ 0.02 0. 0. 0. -0.2 ]]
epsilon: [[ 1.]
[-1.]
[ 1.]
[-1.]
[ 1.]]
Using the following parameters for gLV simulation: {'num_species': 5, 'mu': array([1.27853844, 0.55683415, 2.06752757, 0.86387608, 0.70448068]), 'M': array([[-0.05 , 0. , -0.025, 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , -0.1 , 0. , 0.05 , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , -0.15 , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.01 , 0. ],
[ 0.02 , 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.2 ]]), 'epsilon': array([[ 1.],
[-1.],
[ 1.],
[-1.],
[ 1.]])}
Using the following parameters for gLV simulation: {'num_species': 5, 'mu': array([1.27853844, 0.55683415, 2.06752757, 0.86387608, 0.70448068]), 'M': array([[-0.05 , 0. , -0.025, 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , -0.1 , 0. , 0.05 , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , -0.15 , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.01 , 0. ],
[ 0.02 , 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.2 ]]), 'epsilon': array([[ 1.],
[-1.],
[ 1.],
[-1.],
[ 1.]])}
Using the following parameters for gLV simulation: {'num_species': 5, 'mu': array([1.27853844, 0.55683415, 2.06752757, 0.86387608, 0.70448068]), 'M': array([[-0.05 , 0. , -0.025, 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , -0.1 , 0. , 0.05 , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , -0.15 , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.01 , 0. ],
[ 0.02 , 0. , 0. , 0. , -0.2 ]]), 'epsilon': array([[ 1.],
[-1.],
[ 1.],
[-1.],
[ 1.]])}
[ ]: